What was common in eastern bloc nations apex? This question delves into the defining characteristics that unified the Eastern Bloc, a group of nations under Soviet influence during the Cold War era. From political ideologies to economic structures and social norms, this exploration uncovers the shared traits that shaped these nations’ identities and their place in history.
Eastern Bloc nations exhibited striking similarities in their political systems, characterized by the dominance of communist parties and the suppression of political dissent. Centrally planned economies, with varying degrees of success and challenges, aimed to achieve socialist ideals. Social structures reflected a stratified society, with the state playing a significant role in controlling social mobility and life.
Political Systems
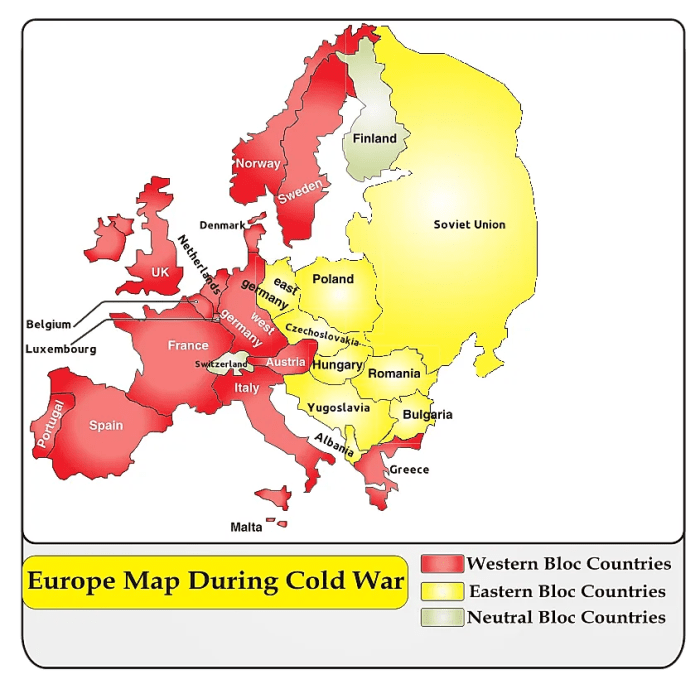
Eastern Bloc nations were characterized by authoritarian political systems, typically led by a communist party that held a monopoly on power. The dominant political ideology was Marxism-Leninism, which emphasized the central role of the state in controlling the economy and society.
Communist Parties and Suppression of Dissent
- Communist parties in Eastern Bloc nations were the sole legal political parties, ensuring the ruling elite’s unchallenged authority.
- Political dissent was severely suppressed through censorship, surveillance, and imprisonment of dissidents.
- Examples: The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) in the USSR, the Polish United Workers’ Party (PZPR) in Poland, and the Socialist Unity Party (SED) in East Germany.
Economic Policies
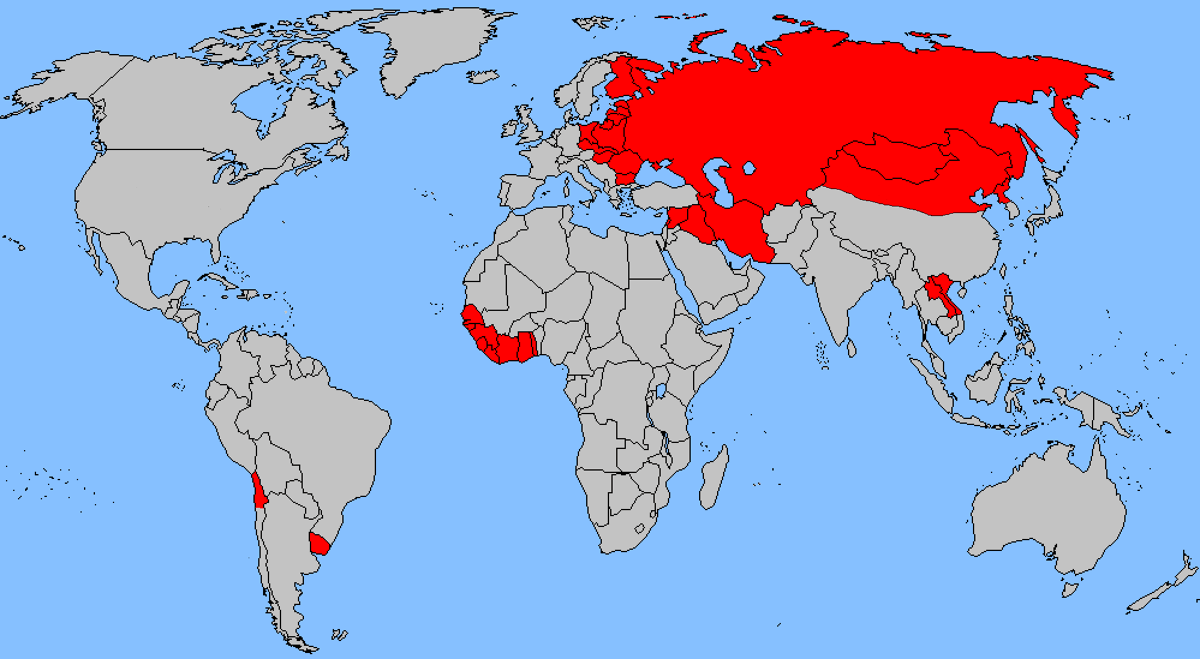
Eastern Bloc nations implemented centrally planned economies, where the state controlled all aspects of economic activity, including production, distribution, and prices. The goal was to create a socialist society free from capitalist exploitation.
Goals and Challenges of Centrally Planned Economies
- Goals:Industrialization, rapid economic growth, and the provision of basic necessities to all citizens.
- Challenges:Inefficiency, lack of innovation, and shortages of consumer goods due to centralized decision-making and rigid planning.
- Examples:The Soviet Five-Year Plans, the Polish Six-Year Plan, and the East German Seven-Year Plan.
Successes and Failures
Centrally planned economies achieved some successes, such as rapid industrialization and high employment rates. However, they also faced significant failures, including chronic shortages of consumer goods, technological stagnation, and environmental degradation.
Social Structures
Eastern Bloc nations exhibited distinct social stratification and class systems, with the communist party elite at the top and the working class at the bottom. The state played a dominant role in controlling social life and mobility.
State Control of Social Life and Mobility, What was common in eastern bloc nations apex
- The state controlled access to education, housing, and healthcare, reinforcing the social hierarchy.
- Social mobility was limited, with individuals largely confined to their class of origin.
- Examples: The nomenklatura class in the USSR, the intelligentsia in Poland, and the working class in East Germany.
Impact on Individuals and Families
The social structures of Eastern Bloc nations had a profound impact on individuals and families. The lack of social mobility limited opportunities for personal growth and fulfillment. The state’s control over social life created a climate of fear and conformity.
Cultural Influences: What Was Common In Eastern Bloc Nations Apex
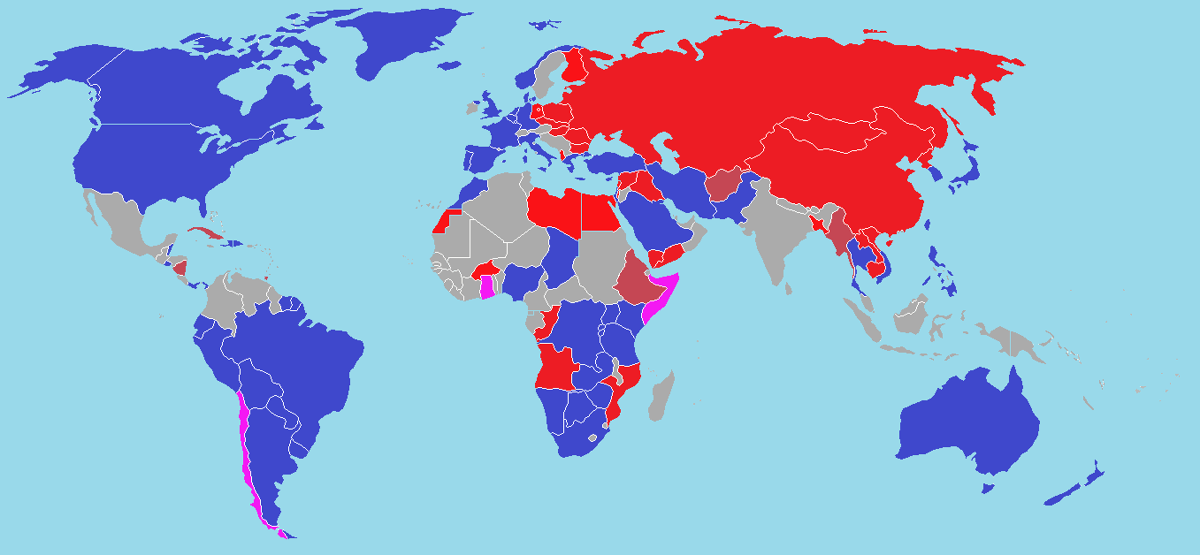
Eastern Bloc nations shared cultural similarities and differences, influenced by both local traditions and Soviet culture and ideology. Soviet influence was particularly strong in areas such as art, literature, and education.
Soviet Influence and Censorship
- Soviet culture and ideology permeated Eastern Bloc societies through propaganda, education, and cultural exchanges.
- Censorship was widespread, suppressing artistic expression that deviated from the official communist line.
- Examples: The Socialist Realism art movement, the banning of books and films critical of the regime, and the imprisonment of dissident artists.
Answers to Common Questions
What was the primary political ideology of Eastern Bloc nations?
Communism, emphasizing the collective ownership of property and the absence of social classes.
How did Eastern Bloc nations implement economic policies?
Through centrally planned economies, where the state controlled production and distribution.
What was the role of the state in Eastern Bloc societies?
The state played a dominant role in controlling social life, mobility, and cultural expression.
