Which of the following is true regarding the income statement? Dive into the intricacies of this fundamental financial document, uncovering its components, structure, accounting principles, and limitations. From revenue recognition to stakeholder analysis, this comprehensive guide illuminates the critical role of income statements in assessing business performance.
In this in-depth exploration, we unravel the complexities of income statements, providing a clear understanding of their significance in the financial landscape.
Components of an Income Statement
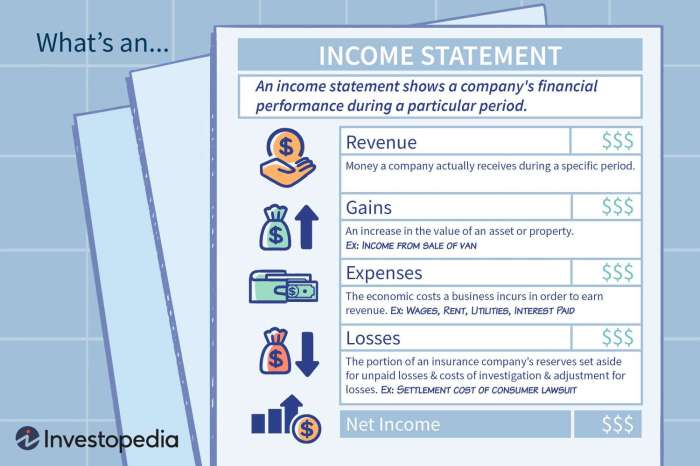
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It presents the income and expenses incurred by the company during that period, culminating in the calculation of net income or loss.The
income statement is divided into three major sections:
- Revenue: This section includes all the income earned by the company from its primary business activities, such as sales of goods or services.
- Expenses: This section lists all the costs and expenses incurred by the company in generating revenue. Expenses can be categorized into various types, including cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and interest expenses.
- Net Income: This is the final figure on the income statement, calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. Net income represents the company’s profit or loss for the period.
Structure of an Income Statement: Which Of The Following Is True Regarding The Income Statement
Income statements follow a standard format that ensures consistency and comparability across different companies and industries. The structure typically includes the following components:
- Header: The header includes the company’s name, the period covered by the statement, and the type of statement (e.g., income statement, consolidated income statement).
- Revenue: Revenue is presented at the top of the statement, followed by deductions for returns, discounts, and allowances.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing or acquiring the goods sold during the period.
- Gross Profit: Gross profit is calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue.
- Operating Expenses: Operating expenses include all non-production costs incurred in running the business, such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Other Income/Expense: This section includes non-operating income or expenses that are not directly related to the company’s core business activities.
- Net Income: Net income is the final figure on the statement, representing the company’s profit or loss for the period.
Accounting Principles and Income Statements
The preparation of income statements is governed by a set of accounting principles that ensure accuracy, consistency, and transparency. These principles include:
- Accrual Accounting: Accrual accounting requires companies to recognize revenue when it is earned and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
- Matching Principle: The matching principle states that expenses should be matched to the revenues they generate in the same period.
- Consistency Principle: The consistency principle requires companies to use the same accounting methods from period to period to ensure comparability of financial statements.
Uses of Income Statements

Income statements are a vital tool for various stakeholders, including:
- Investors: Investors use income statements to assess a company’s profitability and financial health.
- Creditors: Creditors rely on income statements to evaluate a company’s ability to repay debt.
- Managers: Managers use income statements to monitor the company’s performance and make informed decisions.
- Analysts: Analysts use income statements to compare companies within an industry and identify trends.
Limitations of Income Statements
While income statements provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance, they also have certain limitations:
- Income Smoothing: Companies may engage in income smoothing to present a more consistent earnings trend, which can mask underlying financial issues.
- Non-Cash Items: Income statements do not fully capture non-cash items, such as depreciation and amortization, which can affect a company’s profitability.
- Timeliness: Income statements are historical documents that may not reflect the most up-to-date financial information.
FAQ
What is the primary purpose of an income statement?
An income statement provides a summary of a company’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year.
How does accrual accounting impact income recognition?
Accrual accounting recognizes revenue when it is earned and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of cash flow.
What are the limitations of using income statements as a standalone measure of financial performance?
Income statements are subject to manipulation and may not fully reflect a company’s financial health. They do not provide information about cash flow or non-operating activities.
