Label the structures of the bone using the hints provided – Labeling the structures of the bone using the hints provided is a fundamental skill in the field of anatomy. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the anatomical landmarks, microscopic structure, mechanical properties, and formation and remodeling of bones, empowering readers with a thorough understanding of this essential aspect of human biology.
Through a meticulous examination of the various components of bones, this guide unravels the intricate relationship between their structure and function, highlighting the significance of bone anatomy in surgical procedures, disease diagnosis, and the development of therapeutic interventions.
Anatomical Landmarks of the Bone
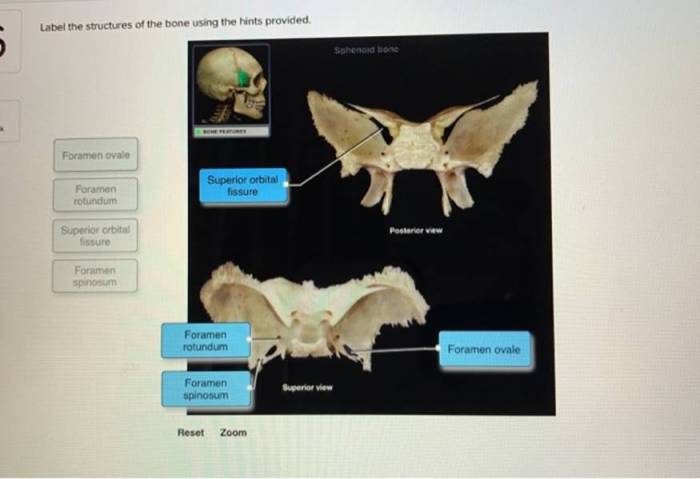
The surface of a bone is marked by various anatomical landmarks that serve as reference points for bone identification, surgical procedures, and understanding bone function. These landmarks include articular surfaces, processes, and foramina.
Articular Surfaces
- Facets: Flat, smooth areas that articulate with other bones
- Condyles: Rounded, knob-like projections
- Trochleae: Groove-shaped surfaces that articulate with ridges on adjacent bones
Processes
- Tuberosities: Rounded, knob-like projections that provide attachment for muscles
- Spines: Sharp, pointed projections that serve as attachment sites for ligaments
- Foramina: Holes or openings that allow passage of blood vessels, nerves, or tendons
Foramina
- Nutrient Foramen: Allows blood vessels to enter the bone
- Articular Foramen: Connects joint cavities with synovial fluid
- Venous Foramen: Allows veins to exit the bone
Microscopic Structure of the Bone: Label The Structures Of The Bone Using The Hints Provided
Bone is a highly organized tissue with a complex microscopic structure. It consists of different types of bone cells and a hierarchical arrangement of bone tissue.
Bone Cells
- Osteoblasts: Cells that synthesize and secrete new bone matrix
- Osteocytes: Mature bone cells that maintain bone structure and regulate bone remodeling
- Osteoclasts: Cells that resorb bone tissue
Hierarchical Organization of Bone Tissue
- Lamellae: Thin, concentric layers of mineralized bone matrix
- Osteons: Cylindrical units of bone tissue containing lamellae arranged around a central canal
- Haversian Systems: Osteons along with their surrounding interstitial bone
Mechanical Properties of Bone
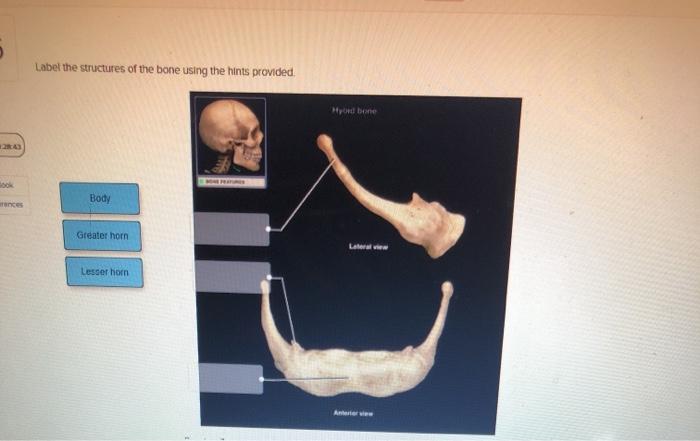
Bone possesses unique mechanical properties that enable it to withstand various forces and perform its functions. These properties include strength, toughness, and elasticity.
Strength
Bone is strong and resistant to compression and bending forces due to its high mineral content and organized structure.
Toughness
Bone is tough and can absorb energy without fracturing due to its hierarchical organization and the presence of collagen fibers.
Elasticity
Bone exhibits elasticity and can deform under stress and return to its original shape upon release, contributing to its shock-absorbing capacity.
Bone Formation and Remodeling
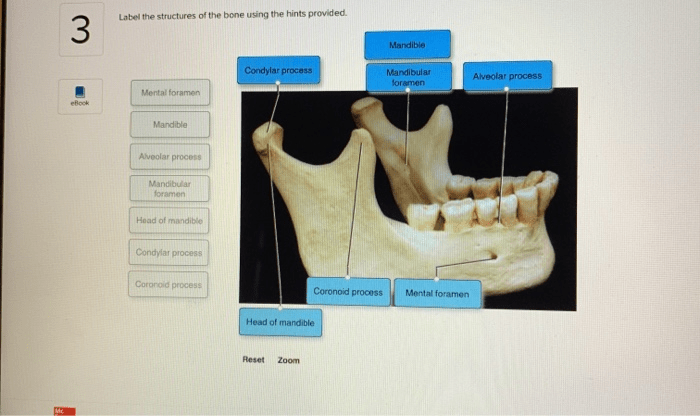
Bone is a dynamic tissue that undergoes continuous formation and remodeling throughout life. These processes ensure bone growth, repair, and adaptation to changing mechanical demands.
Bone Formation
Bone formation occurs through a process called ossification, where osteoblasts lay down new bone matrix.
Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling involves the resorption of old bone by osteoclasts and the formation of new bone by osteoblasts, maintaining bone strength and adapting it to functional needs.
Bone Diseases and Disorders
Various diseases and disorders can affect bone health and function. Understanding these conditions is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Osteoporosis, Label the structures of the bone using the hints provided
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by decreased bone density, making bones weak and susceptible to fractures.
Paget’s Disease
Paget’s disease is a chronic bone disorder that leads to abnormal bone remodeling, resulting in weakened and deformed bones.
Bone Cancer
Bone cancer, such as osteosarcoma and myeloma, can affect bone structure and function, causing pain, weakness, and potential metastasis.
Detailed FAQs
What are the major anatomical landmarks of a bone?
Major anatomical landmarks of a bone include articular surfaces, processes, and foramina, which serve as attachment points for muscles, ligaments, and tendons, and provide passage for nerves and blood vessels.
What are the different types of bone cells?
Bone cells include osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts, each playing specific roles in bone formation, maintenance, and resorption.
What factors influence the mechanical properties of bone?
Factors influencing bone’s mechanical properties include its density, porosity, and the alignment of collagen fibers, which determine its strength, toughness, and elasticity.