Lewis structures of atoms worksheet – Embark on a journey into the realm of Lewis structures of atoms, a fundamental concept in chemistry that unveils the intricate dance of electrons and the formation of chemical bonds. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of Lewis structures, empowering you with the knowledge to decipher the electronic configurations of atoms and predict their bonding behavior.
Delving deeper, we explore the practical applications of Lewis structures, demonstrating their utility in comprehending chemical reactions and predicting molecular properties. Interactive exercises and real-world examples bring the concepts to life, fostering a profound understanding of this essential tool in chemistry.
Introduction to Lewis Structures
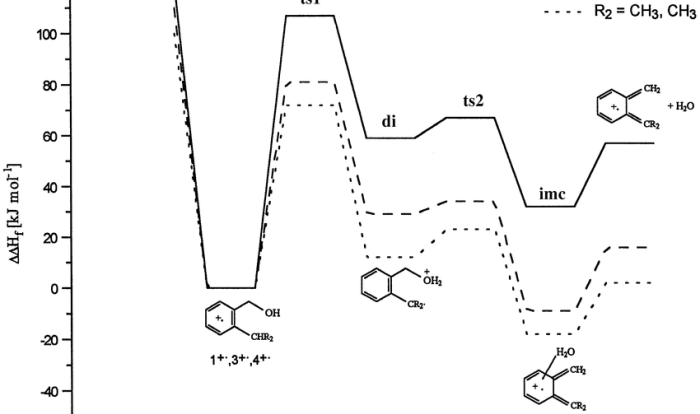
Lewis structures are a graphical representation of the electron arrangement in atoms and molecules. They provide a visual representation of the number of valence electrons, their arrangement around the atom, and the bonding between atoms.The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until they have a full valence shell of eight electrons.
This rule applies to most elements in the periodic table, except for hydrogen and helium, which are stable with two valence electrons.
Application of the Octet Rule, Lewis structures of atoms worksheet
The octet rule can be used to predict the Lewis structure of an atom or molecule. For example, consider the element carbon. Carbon has four valence electrons. To achieve a full valence shell, it must gain or share four electrons.
One possible Lewis structure for carbon is:“`:C:“`In this Lewis structure, the carbon atom is surrounded by four dots, representing the four valence electrons.
Drawing Lewis Structures of Atoms
Lewis structures, also known as electron dot structures, provide a graphical representation of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule. Drawing Lewis structures for atoms involves understanding the basic principles of electron configurations and bonding. Here are the steps involved:
- Determine the number of valence electrons:Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and they participate in chemical bonding. The number of valence electrons can be found by using the periodic table.
- Arrange the valence electrons as dots around the atomic symbol:Each dot represents a single valence electron. The dots should be placed around the atomic symbol in a symmetrical manner, avoiding any lone pairs.
- Complete the octet for each atom:Most atoms aim to achieve a stable electron configuration by having eight valence electrons (an octet). If an atom has less than eight valence electrons, it will tend to gain or share electrons to complete its octet.
Here are some examples of Lewis structures for different atoms:
- Hydrogen (H): H
- Helium (He): :He:
- Lithium (Li): Li.
- Carbon (C): :C:
- Nitrogen (N): :N:
- Oxygen (O): :O:
- Fluorine (F): :F:
Using Lewis Structures to Predict Bonding
Lewis structures can be used to predict the bonding behavior of atoms by determining the number of valence electrons available for bonding. Atoms with unpaired valence electrons are likely to form bonds to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons (the octet rule).
Relationship between Lewis Structures and Molecular Geometry
The Lewis structure of a molecule provides insight into its molecular geometry. The number and arrangement of electron pairs around the central atom determine the shape of the molecule. For example, a molecule with four electron pairs around the central atom will have a tetrahedral geometry, while a molecule with three electron pairs will have a trigonal planar geometry.
Applications of Lewis Structures

Lewis structures provide a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of atoms and molecules. They can be used to illustrate chemical reactions, predict molecular properties, and explain the bonding between atoms.
Using Lewis Structures to Understand Chemical Reactions
Lewis structures can be used to illustrate chemical reactions by showing the movement of electrons between atoms. For example, the reaction between sodium and chlorine can be represented as follows:
Na + Cl → NaCl
The Lewis structures for sodium and chlorine are:
Na: [Ne] 3s1Cl: [Ne] 3s 23p 5
When sodium and chlorine react, the sodium atom transfers its single valence electron to the chlorine atom, forming a sodium ion (Na +) and a chloride ion (Cl –). The Lewis structures for the ions are:
Na+: [Ne]Cl –: [Ne] 3s 23p 6
The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other, forming sodium chloride (NaCl).
Using Lewis Structures to Predict Molecular Properties
Lewis structures can also be used to predict molecular properties, such as shape, polarity, and bond strength. The shape of a molecule is determined by the number of electron pairs around the central atom. For example, a molecule with four electron pairs around the central atom will have a tetrahedral shape.
The polarity of a molecule is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the atoms. A molecule is polar if the electronegativity difference between the atoms is greater than 0.5. A molecule is nonpolar if the electronegativity difference between the atoms is less than 0.5.
The bond strength of a molecule is determined by the number of bonds between the atoms and the type of bonds. A single bond is weaker than a double bond, which is weaker than a triple bond. A bond between two atoms of the same element is stronger than a bond between two atoms of different elements.
Advanced Concepts in Lewis Structures
As we delve deeper into the world of Lewis structures, we encounter more complex concepts that extend our understanding of chemical bonding.
One such concept is resonance, which arises when a molecule can be represented by multiple valid Lewis structures that differ in the placement of electrons. In such cases, the actual electronic structure of the molecule is a hybrid of these resonance structures, resulting in a delocalization of electrons.
Limitations of Lewis Structures
While Lewis structures provide a valuable tool for understanding chemical bonding, they do have certain limitations.
One limitation is that Lewis structures cannot fully describe the bonding in molecules with delocalized electrons, such as those involved in resonance. In these cases, the Lewis structure may not accurately represent the true electronic distribution.
Another limitation is that Lewis structures do not explicitly account for the three-dimensional geometryof molecules. While the octet rule provides a useful guideline for predicting the number of bonds an atom can form, it does not specify the spatial arrangement of these bonds.
Interactive Practice and Examples
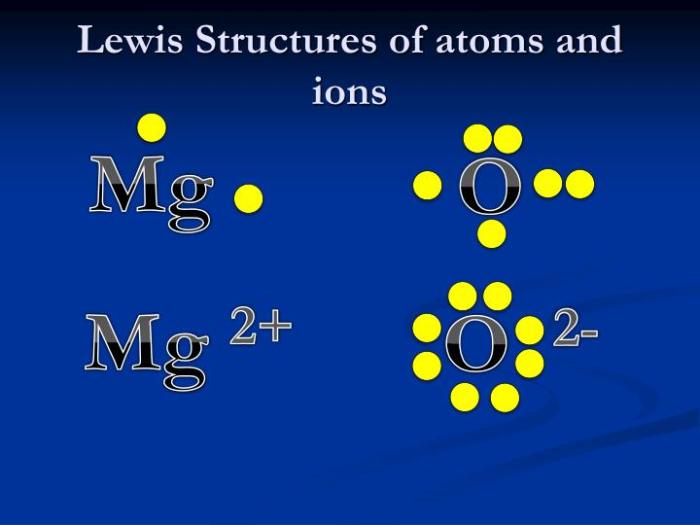
Interactive practice and real-world examples play a crucial role in reinforcing the understanding of Lewis structures. They provide students with opportunities to apply their knowledge, identify their strengths and weaknesses, and connect theoretical concepts to practical applications.
Interactive Exercises and Worksheets
Interactive exercises and worksheets can be designed to provide students with hands-on practice in drawing Lewis structures. These exercises can include:
- Identifying the number of valence electrons for a given atom or ion
- Arranging valence electrons in a Lewis dot structure
- Determining the shape of a molecule based on its Lewis structure
- Predicting the bonding behavior of atoms based on their Lewis structures
Real-World Examples
Lewis structures find applications in various fields, including:
- Chemistry:Understanding the electronic structure of molecules, predicting chemical bonding, and explaining chemical reactions
- Biology:Studying the structure and function of biological molecules, such as proteins and DNA
- Materials Science:Designing new materials with specific properties by manipulating the electronic structure of atoms
li> Pharmacology:Developing new drugs by understanding the interactions between molecules and biological targets
Commonly Asked Questions: Lewis Structures Of Atoms Worksheet
What are Lewis structures?
Lewis structures are diagrams that depict the arrangement of electrons around atoms, providing insights into their bonding behavior.
How do I draw Lewis structures?
Drawing Lewis structures involves determining the number of valence electrons, arranging them around the atomic symbol, and connecting atoms with lines to represent shared electron pairs.
What is the significance of the octet rule in Lewis structures?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons, which is represented in Lewis structures.
How can Lewis structures predict bonding?
Lewis structures can predict bonding by indicating the number of shared electron pairs between atoms, which determines the type and strength of the bond.
What are the limitations of Lewis structures?
While Lewis structures provide valuable insights, they may not accurately describe certain molecules, such as those involving resonance or hypervalent atoms.